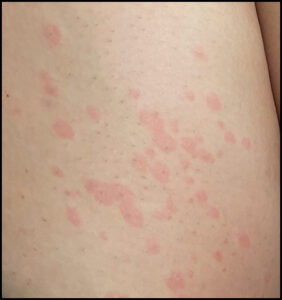
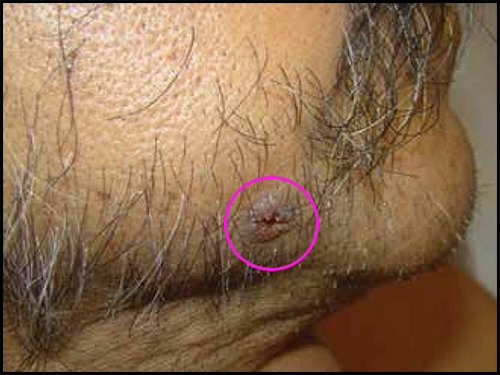
If you get infected with Cocci, it may affect you in a number of ways. You may not get sick at all; you might have a mild lung problem; or, more rarely, you will have serious complications. Read on to learn about how Cocci may affect you.

Who Gets Sick and Who Gets Diagnosed?
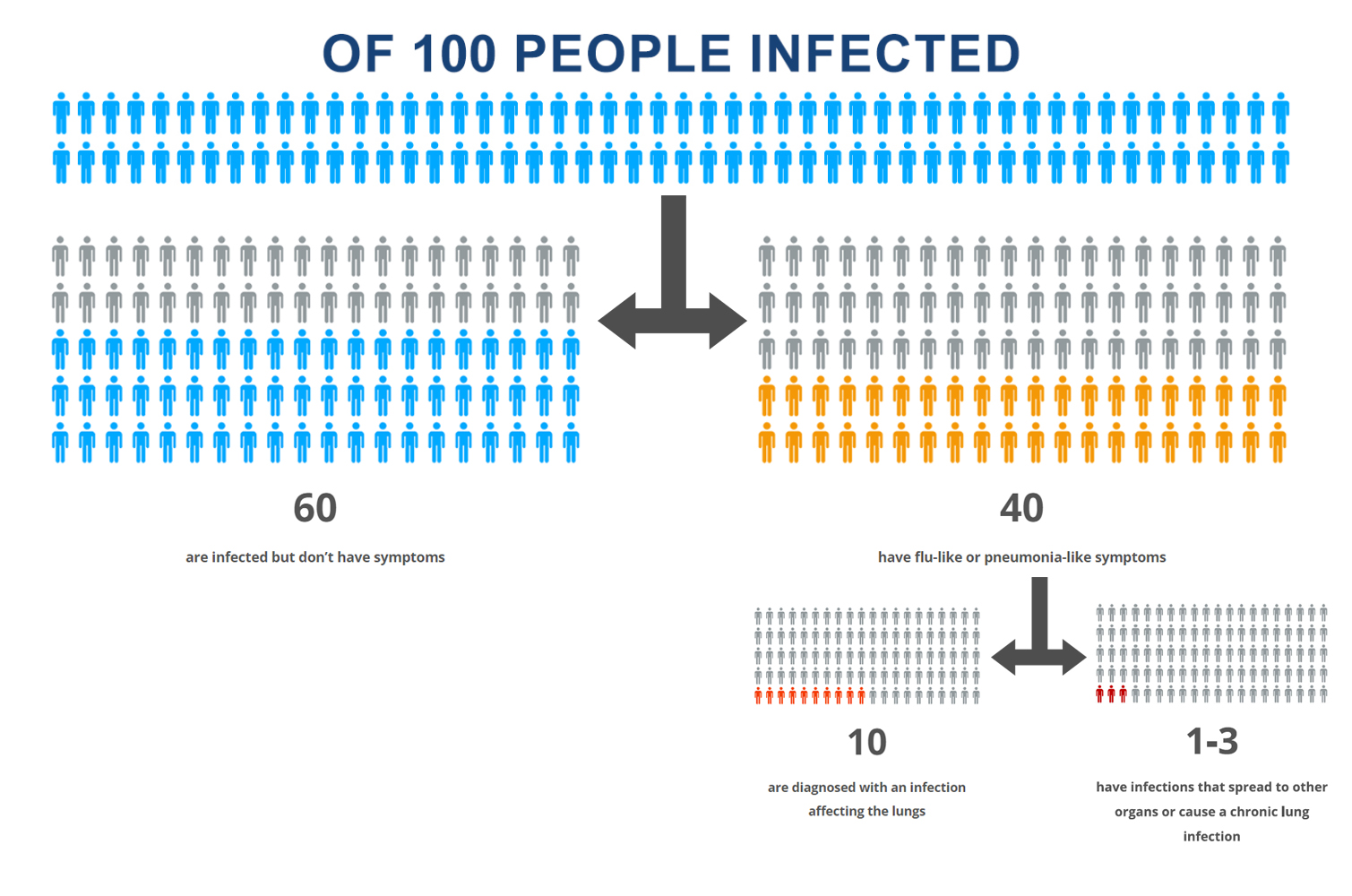
Before we get into the symptoms of coccidioidomycosis (Cocci), it’s important to appreciate that not everyone who is infected with Cocci gets sick. Let’s take a look at the numbers (Figure 1). When we think about Cocci, the most common presentation is a mild lung illness like a cold or flu but lasting noticeably longer. Chronic or complex lung issues or infections occurring outside the lungs are less common.
Figure 1. Typical distribution of Cocci cases in 100 infected people.
Valley Fever Symptoms
Let’s start by looking at those 40% of patients who have flu-like or pneumonia-like symptoms. This is the group of people affected by Valley Fever. Symptoms usually start about two weeks after exposure. Figure 2 shows the common symptoms associated with Valley Fever.
Figure 2. Common Symptoms Associated With Valley Fever

Fatigue

Cough

Shortness of breath (or Chest pain)

Fever

Night sweats
Muscle or joint pain

Weight loss
Rash

Headache

Loss of Appetite
Chronic Pulmonary or Disseminated Cocci
Sometimes the primary Cocci infection of the lungs is complicated, does not go away (chronic pulmonary Cocci), or spreads (disseminates) from the lung to other organs. Patients with disseminated disease typically have symptoms that last a long time after the infection. As shown in Figure 3, Cocci typically spreads to the skin, bones, brain, and the meninges. Chronic or complicated pulmonary or dissemination Cocci can lead to a range of symptoms as shown in the Table.
Figure 3. Sites of Cocci dissemination
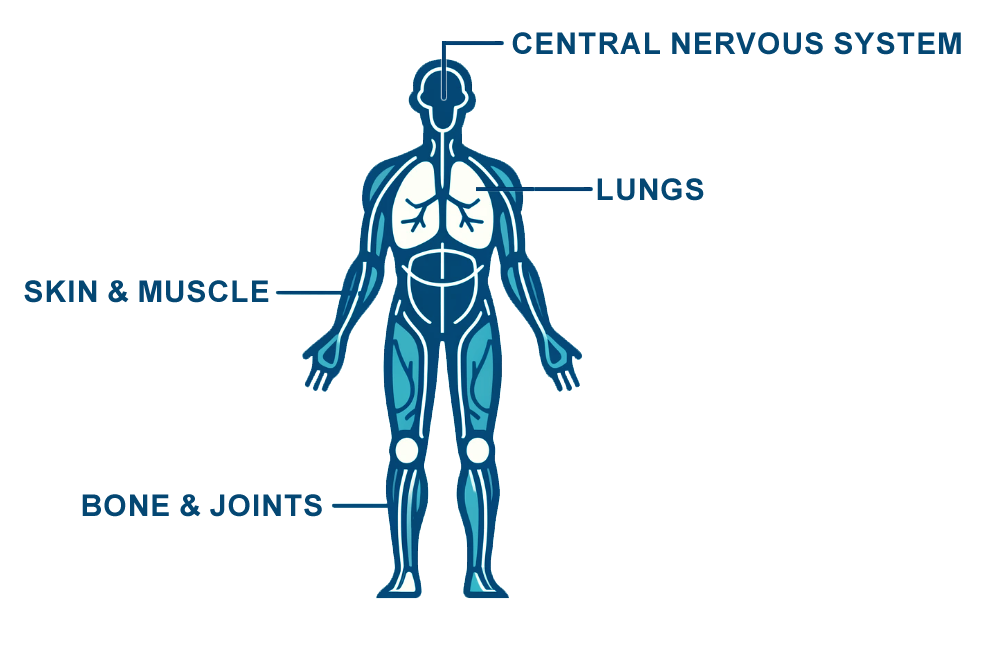
Table: Areas of involvement and symptoms of chronic, complicated, or disseminated Cocci. Note the symptoms that are considered red flags are bolded and marked. These symptoms need urgent treatment and evaluation.
Area Involved |
Symptom |
| Complicated or chronic pulmonary disease | Chronic cough, weight loss, chest pain, trouble breathing, hemoptysis (coughing up blood) |
| Central nervous system (meninges) | Severe headaches, blurred vision, neck stiffness, hearing changes, confusion |
| Skin | Nodules, draining, nonhealing ulcers (breaks in the skin), and abscesses in the skin |
| Lymph node | Swollen or draining lymph node |
| Bone | Pain in the bones, often involving the spine (back bones), leg bones, feet, and skull. These changes can result in height loss, worsening back and neck pain, lower extremity weakness, and hunchback. Sometimes the infection can spread locally, leading to abscesses. |
| Joints | Painful, swollen, warm joints, especially knees or ankles |